RiboNAT™ Rapid Sterility Test
As part of safety testing for pharmaceuticals, sterility tests are conducted to check for microbial contamination. The compendial sterility test method requires a 14-day incubation period, which has increased the demand for faster testing methods, especially for cell-based medicines with short shelf lives. RiboNAT™ utilizes the NAT method (Nucleic Acid Amplification Test) to rapidly detect bacteria and fungi.
Features
- ➢ Short time (7 hours) and high sensitivity (9 CFU/mL).
- ➢ Extracts total RNA of microorganisms and detects ribosomal RNA.
- ➢ Wide range of bacteria and fungi can be detected with a single assay (qualitative test).
- ➢ Reduction of false positives from dead microorganisms and residual DNA.
Assay Flow
- Step 1. Pre-treatment
-
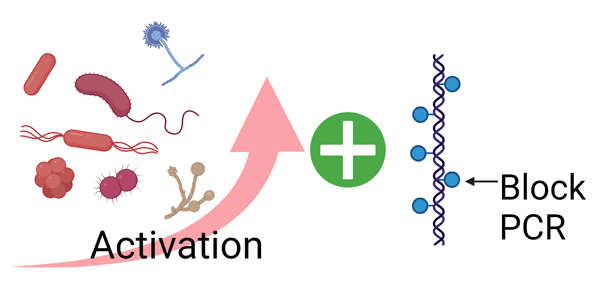
- Activation of microorganisms.
- Inactivation of residual DNA.
3.5 hours- RNA Isolation Kit 1
- Step 2. RNA isolation
-
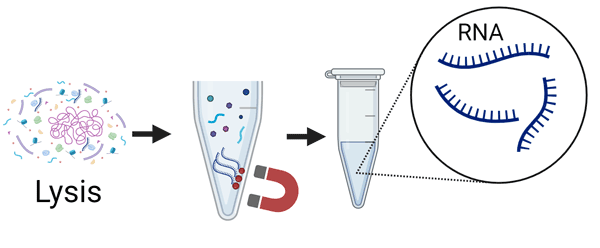
- Lysis of microorganism.
- RNA extraction & purification.
1.5 hours- RNA Isolation Kit 1
- RNA Isolation Kit 2
- Detection Kit
- Step 3. Measurement
-
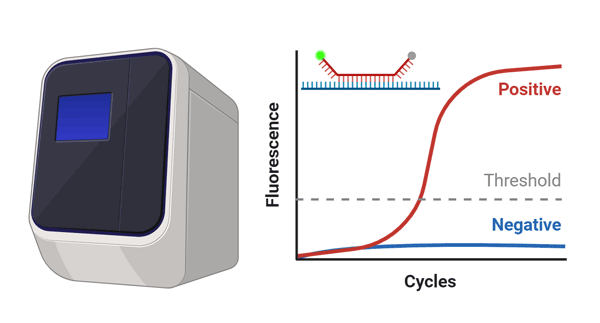
- RNA detection with reverse
transcription real time PCR.
1.2 hours- RNA Isolation Kit 1
- Detection Kit
- RNA detection with reverse
*Illustrations were created with BioRender.
h
o
u
r
s
Performance
Detection of 6 species described in pharmacopeias : Spiked 9 CFU/mL
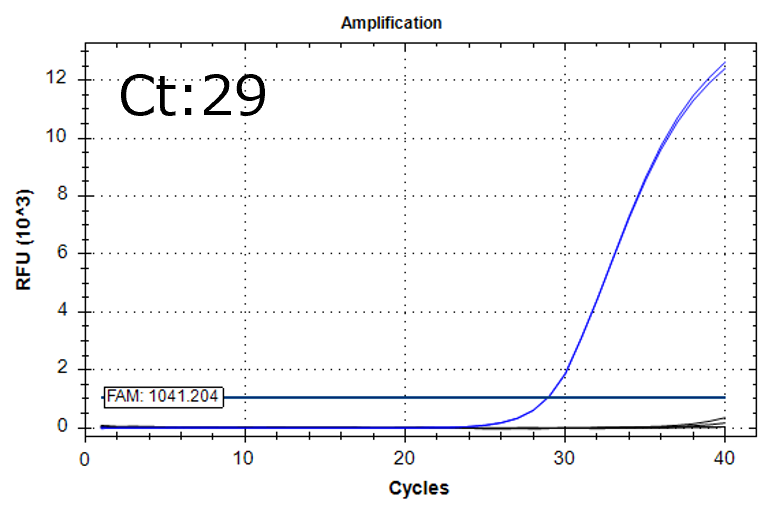
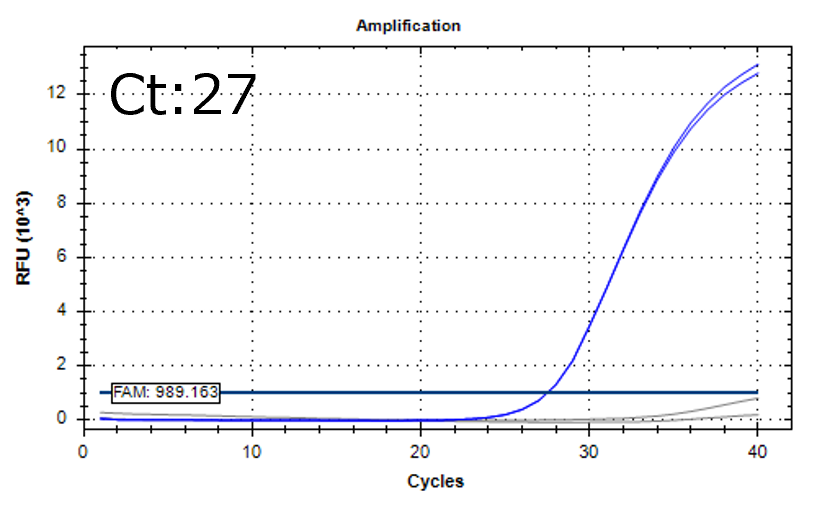
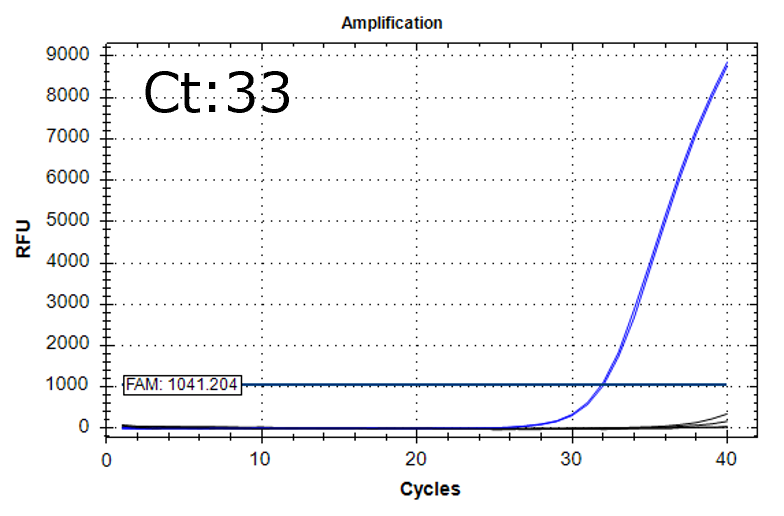
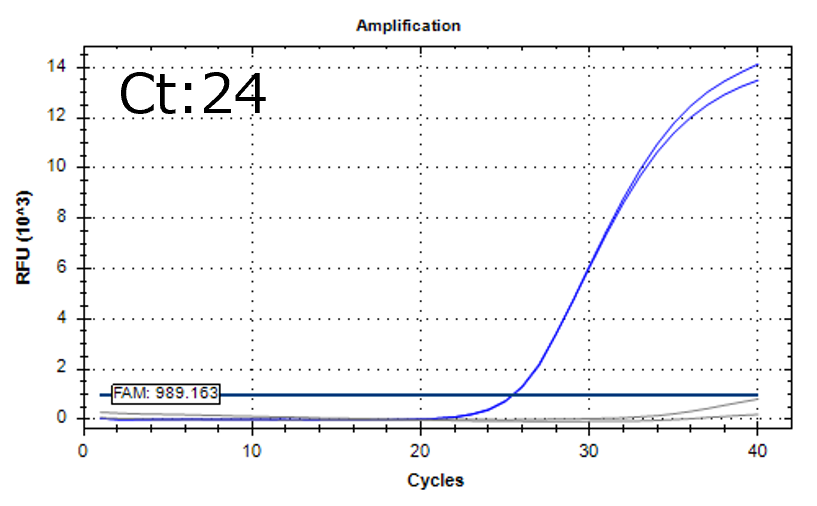
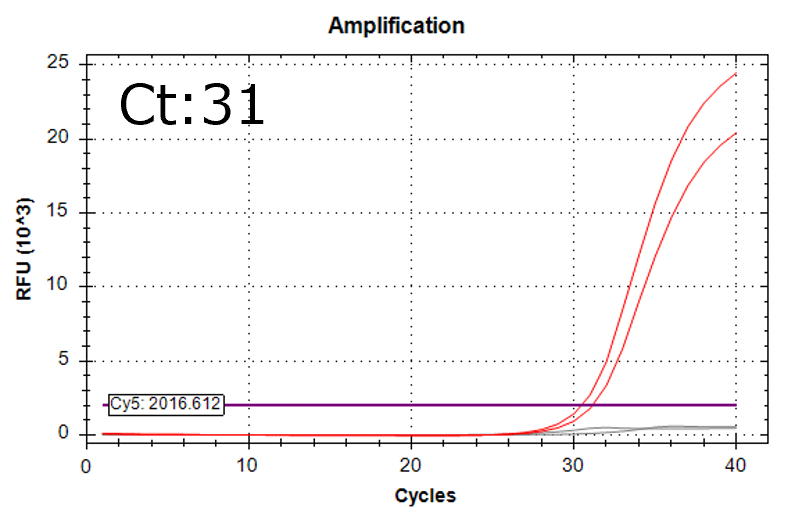
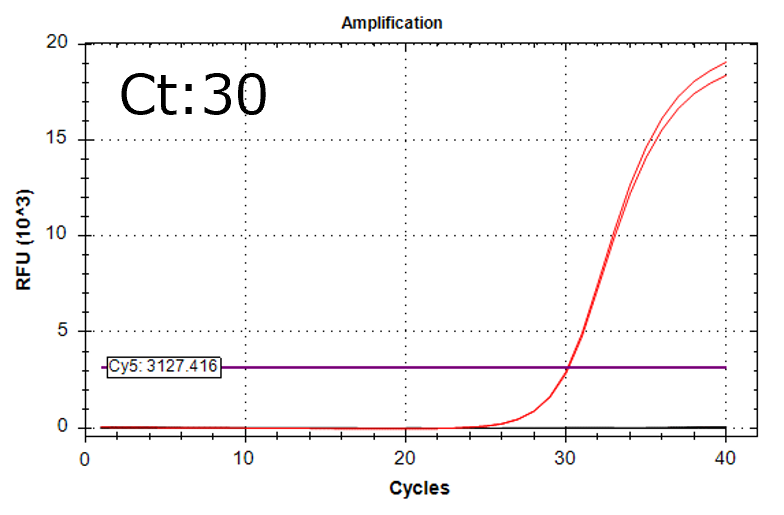
Detectable at 9 CFU/mL
Spiked 9 CFU/mL with cell suspension sample
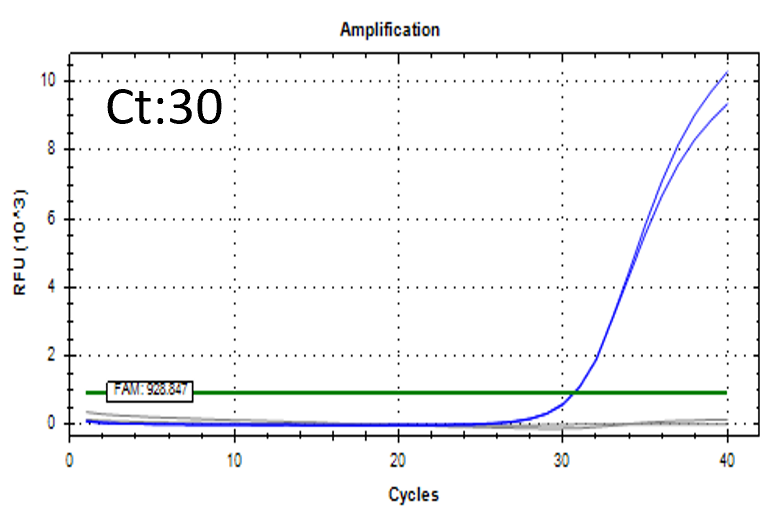
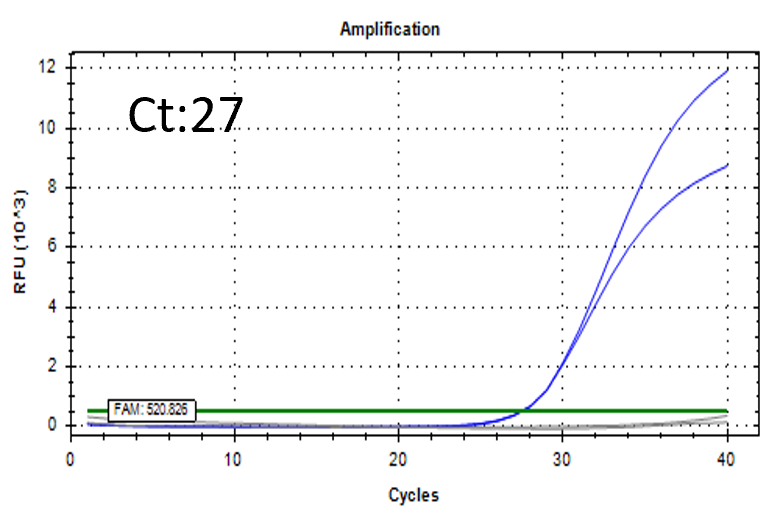
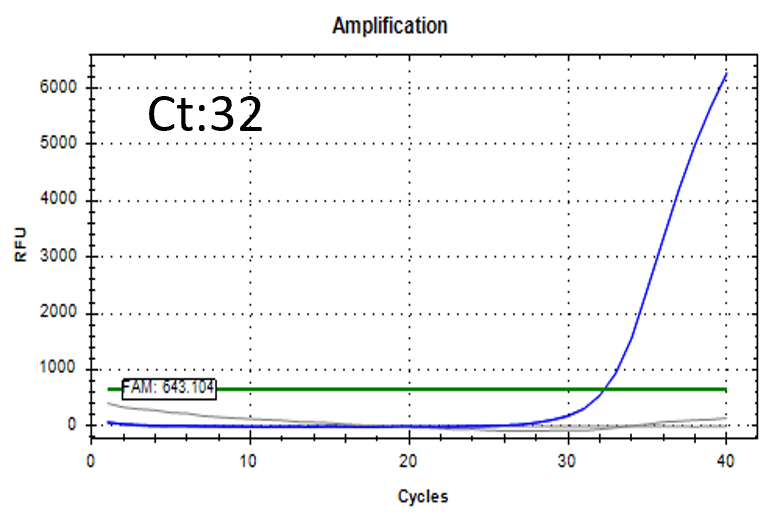
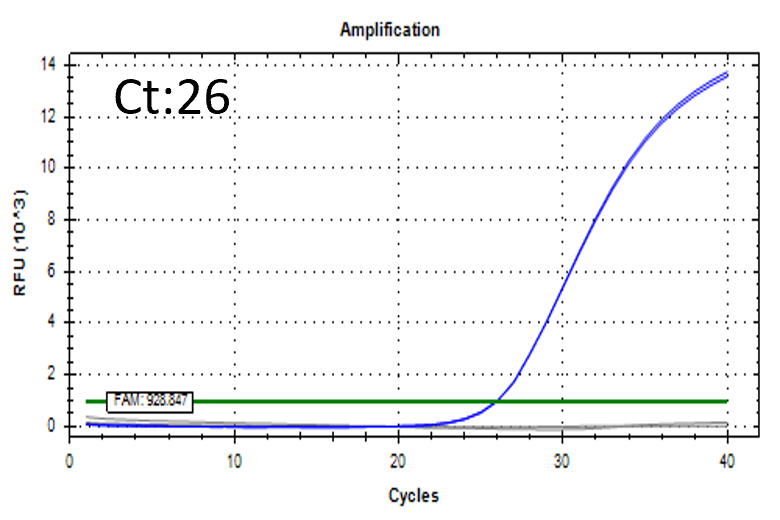
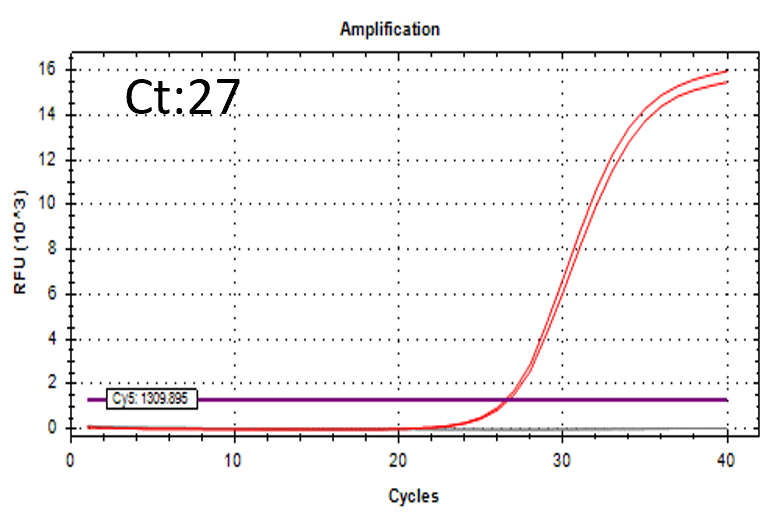
Test condition
- Cells: HEK293
- Concentration: 0.25 x 106 cells/mL
(0.5 x 106 cells /2 mL /assay)
*Detectable also in the below condition
- Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC): 0.5 x 106 cells/mL
- T-cells: 1.0 x 106 cells/mL
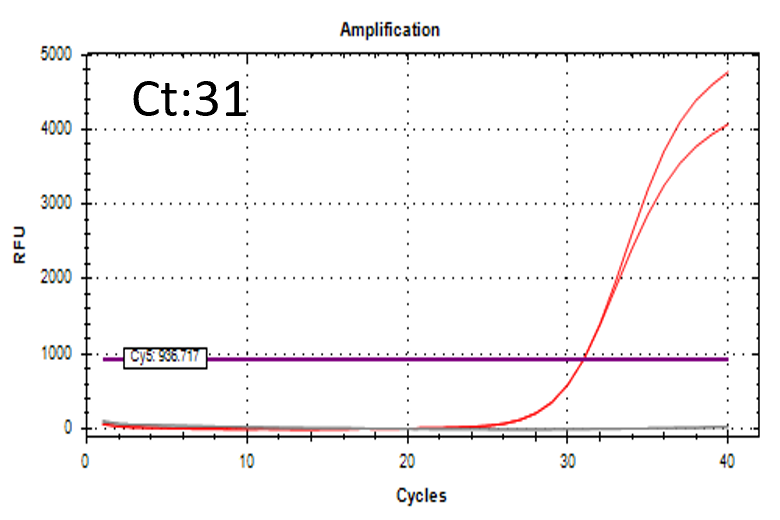
Detectable at 9 CFU/mL with cell suspension sample
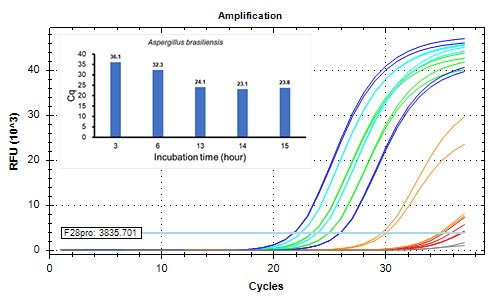
Higher sensitivity method
- Inoculated strain: 2 CFU/mL
- Incubation time: 3-15 hours

BIOBALL®
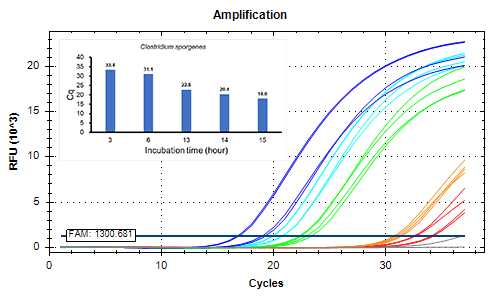
Strain : NCPF2275
< Fungi >
BIOBALL®
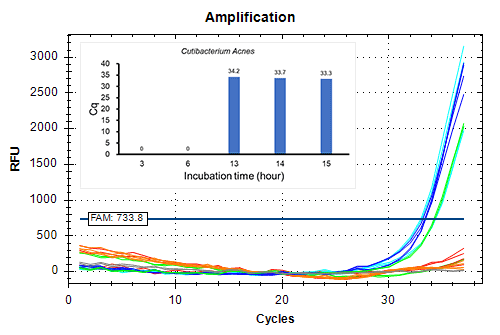
Strain : NCTC12935
< Strictly anaerobic bacteria >
BIOBALL®
Strain : DSM1897
< Facultative anaerobic bacteria,
Doubling time: 5 hrs. >
Detected 2 CFU/mL of strictly anaerobic bacteria and slow growth bacteria by 14 hours or longer incubation.
Extended incubation enhances sensitivity
Reduction of False Positive
RiboNAT™ includes treatment steps with a reagent for inactivating DNA from dead cells and DNase. This process helps reduce false positives caused by residual DNA in the sample.
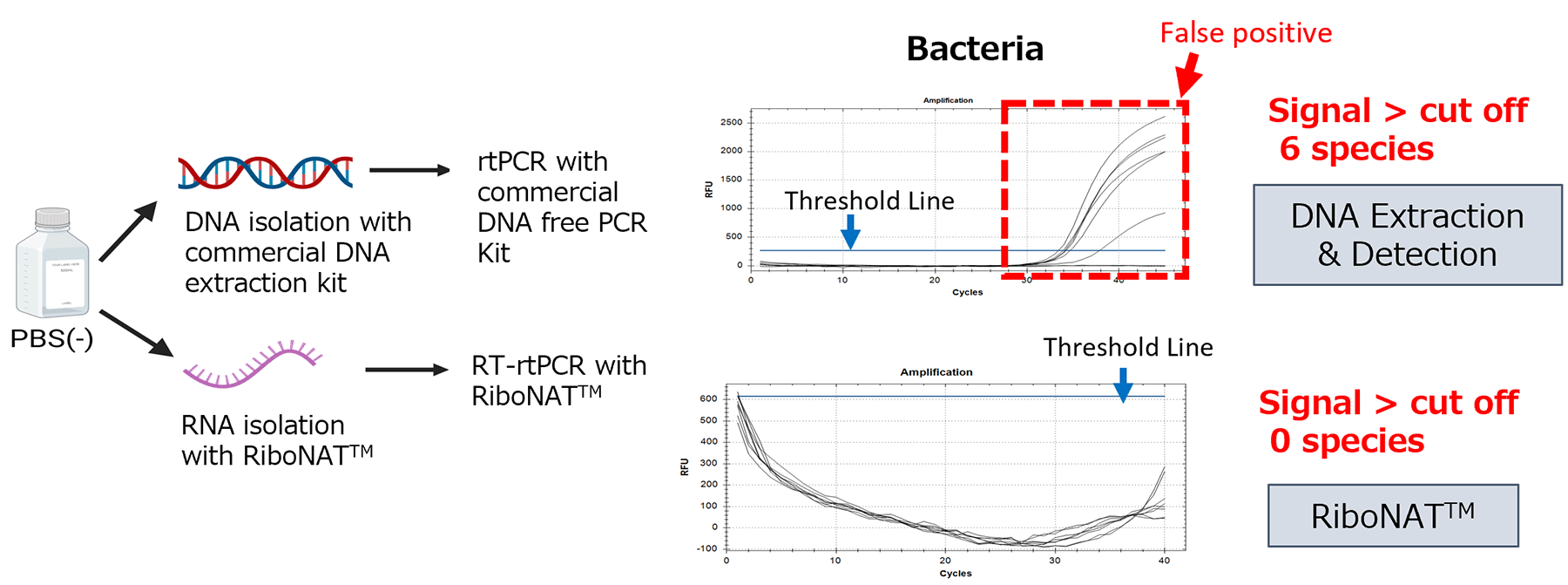
False positive derived from residual DNA was reduced
Specifications of Detection Kit
| Detection method | One step reverse transcription real time PCR with fluorescence probe (RT-rt PCR) |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 100 RNA copies per reaction |
| Coverage* | Bacteria: 25,748 (95.7%) Fungi: 1,683 (92.3%) *In silico analysis, Accepting 3 mismatches, Data bank: Silva |
| Target | Bacteria: 23S Ribosomal RNA (Detection wavelength: 515-530nm) Fungi: 25/28S Ribosomal RNA (Detection wavelength: 675-690 nm) Internal Control: Artifact sequence (Detection wavelength: 560-580 nm) |
Instruction Video
Kit component
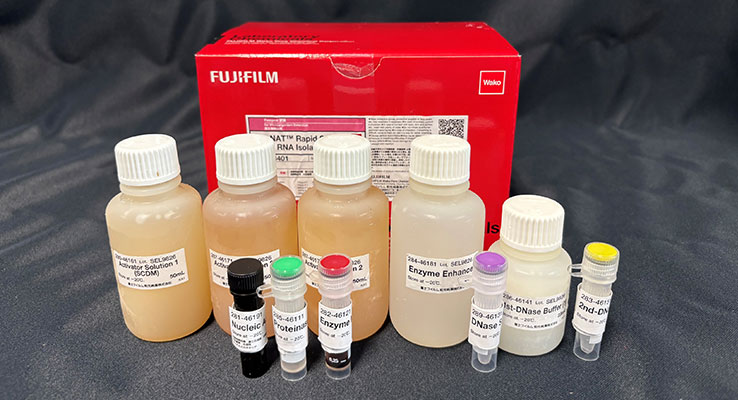

- Activator Solution 1 (SCDM)
- Activator Solution 2 (TG) x 2
- Enzyme Enhancer
- DNase Solution
- 1st-DNase Buffer (1)
- 2nd-DNase Buffer (2)
- Nucleic Acid Inactivator
- Proteinase K Solution
- Enzyme Mix
- Binding Buffer
- 1st-Wash Buffer (1)
- 2nd-Wash Buffer (2)
- Lysis Buffer
- Lytic Enhancer
- Elution Buffer x 3
- Magnetic Beads
- Sample Tube x 2
- Elution Tube
- Water
- Positive Control RNA
- Internal Control RNA
- Detection Mix x 2
※RiboNAT™ RNA Isolation Kit 1, RNA Isolation Kit 2, Detection Kit are all required for the assay.



